As you know, Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) aims to build systems that can match or surpass our human mind across many tasks—and mind you, we are not simply talking about some narrow ones like translation or chess. It’s about creating AGI technologies and AI solutions that can learn skills, solve new problems, and adjust with change.
But this goal is a different kettle of fish—the living, biological intelligence inside the human brain. When you compare these two, you could see what engineers, philosophers, and societies are truly up against: technical limits, questions of consciousness, and the social impact on jobs, education, and policy.
What Is the Human Brain?
Let’s do a quick trivia. Were you able to read the above paragraph? Comprehend what I just told you? And recall what you just understood? You can.But how?
It’s because of the slimy mass present inside of our skulls: the brain.
At the utmost simplest level, our brain is a complex biological organ that allows us to sense, process, store, and act.
Let’s take a look at these fascinating physical facts to help anchor comparison:
- Neuron count: As per the modern estimates, there are roughly 86 billion number of neurons present in an adult brain.
- Connections: Now, these neurons link together through tens of trillions to around a hundred trillion synapses, these are the points where signals are shared among them (these connections change as we learn and grow).
- Energy budget: You’d be astonished to hear that the brain uses the energy of a light bulb for all the work it does, which is roughly 20 watts. Yet, in spite of this little energy, we can think, memorize, and move!
What Do People Mean by AGI and AGI Agents?
In simple terms, AGI means a system that possesses intelligence similar to ours, allowing it to do tasks that we perform. These collaborative AI systems learn and process like us.You must have heard this term, “AGI,” or Artificial General Intelligence, in the talks of marketing and businesses, for a buzzword it has truly become, along with being a term that sparks debate.
In most industries and policy discussions, we refer it to as systems that can handle a wide range of mental tasks—the kind that humans perform—without needing to be rebuilt for each new job. OpenAI, for instance, describes AGI as a system that works on its own (highly autonomous) and can outperform humans in many kinds of valuable work. While this idea might sound simple on paper, creating a machine that can think on its own is easier said than done.
Current Status
What’s important to understand is that true AGI doesn’t exist yet—at least not by any shared scientific agreement that we know. Experts in labs, universities, and newsrooms are still squabbling about what counts as AGI and when it might appear.Some believe we’re close, pointing to large AI models that seem almost general in their abilities. Others insist these systems still fall short in crucial ways. The discussion continues—sharp, restless, and full of possibility.
AI vs AGI
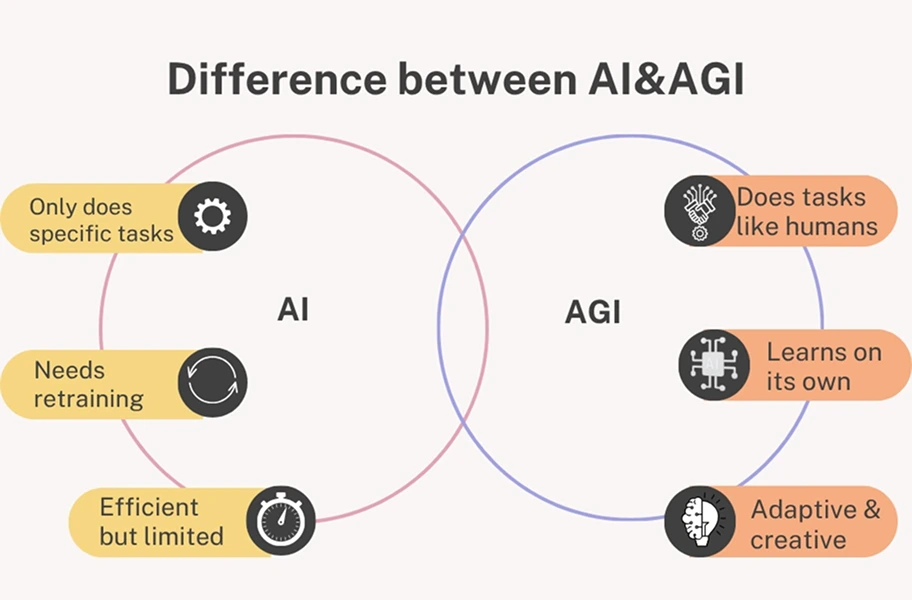
Human Brain vs AI Brain
At a high level, comparing AGI and the brain is comparing two different design classes:| Human Brain Intelligence | AGI |
|---|---|
| It is built on billions of neurons, which work slowly in parallel. | It runs on digital hardware, like CPUs and GPUs. |
| Utilizes chemical signaling, plus adapts by local learning processes. | Has to use algorithms (like neural networks, probabilistic models, and symbolic systems). |
| Very energy-efficient and can learn over a lifetime. | Very swift but takes a lot of energy, plus it’s dependent on datasets. |
| Deeply connected to the body through sensory and motor systems. | Operates through modular systems for storage, computation, and networking. |
| Develops and learns through real-world experiences in a dynamic environment. | Trained using pre-collected data and deployed across distributed servers. |
| Functions as an integrated system, hence mind and body work together. | Works as a separate, modular structure. Can be increased with the addition of hardware. |
| Built to be strong, and adjustable. | Scales mainly through increased data and computing power. |
| Handles new and unpredictable situations flexibly. | Struggles with unfamiliar or untrained scenarios. |
Memory Systems: Working Memory, Long-Term Memory, and Model Weights
Human Memory Systems
Humans rely on several interconnected memory systems:- Sensory memory: it takes in what we see or hear.
- Working memory: it’s like a short-term mental desk; it holds mere abstracts of information at a time.
- Long-term memory: through deep neural connections, it stores knowledge within.
Memory in AI Systems
Artificial intelligence, especially large language models, operates differently:- Model weights: hold compressed knowledge learned during training—like vast libraries written in numbers.
- Context window: serves as short-term memory, containing only the text or data the model can process at a time.
Now, we can conclude that we are able to revisit, reorganize, and strengthen memories through creativity and intent—using repetition, patterns, or meaning. But, on the other end of the spectrum, AI, is very much dependent upon its trained knowledge and a limited window of awareness, making deep, step-by-step reasoning or long-term planning a tougher mountain to climb.
Perception: Human vs. AGI Technology

Human Perception
Did you notice just how effortlessly you clicked upon this blog, have been scrutinizing each and every word, and are making sense of it?You wouldn't be doing this if you didn't have your 5 senses. We experience the world through a rich web of senses, and so, our perception isn’t passive, but alive and always searching.
- Our brain moves our eyes, heads, and hands and basically controls our entire body.
- All the experiences we've had in our past shape what we notice and interpret in the present.
Perception in AI Systems
AI, on the other hand, works totally differently.- It sees through a narrow lens (some focus only on images, others on text or sound).
- New multimodal models are beginning to blend text, visuals, and audio, and sometimes even video.
- AGI models are being designed so that they can also understand emotional and social intelligence.
The Road Ahead
Robotics aims to change that by giving AI a physical form—a way to act and learn from the real world. But as the saying goes, “easier said than done.” Building such embodied systems brings new technical hurdles, though it also brings AI one step closer to truly understanding the world it lives in.Reasoning, Abstraction, and Common Sense
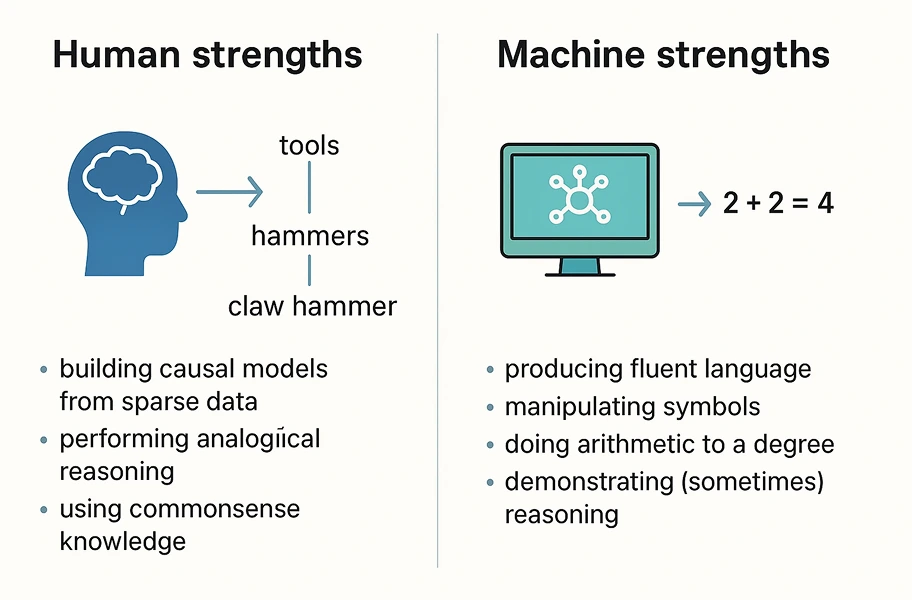
Human Strengths
- People have a natural gift for finding patterns and connections even with little information.
- They draw on lived experience, turning it into quiet wisdom that helps them understand the world.
- Humans can climb the ladder of ideas, linking small details to bigger meanings — like tracing a tool back to its purpose.
Machine Strengths
- Modern AI models are clever pattern imitators that can weave fluent language and handle numbers.
- Their “thinking” is a reflection, not true understanding—they map symbols instead of building meaning.
- At times, like a cracked mirror, they confidently produce answers that look right but aren’t real.
- They act upon data, not understanding, which can lead to concerns in AGI security and AGI governance.
Creativity: Human vs Machine
Human Creativity
- Our creativity produces unique and different mosaics of memories, inspirations, and emotions.
- The way we view and process things, often outstretches regular perspectives, helping us to find meaning and knowledge into things deeply.
- Intuition is there quietly guiding us, and helping us make sense of things before we even realize it.
Machine Creativity
- Machines can make stories, music, or images by reusing patterns from the data they learn.
- Their results can surprise and even impress us.
- But their spark isn’t their own—they don’t feel or imagine.
- Their creativity is more like a reflection in still water—clear, clever, but without life behind it.
Speed, Latency, and Parallelism
| Concept | Human Brain | Machines/AI Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slightly slow compared to a computer since the neurons in our brain fire in milliseconds. | Works with utter speed (measured in billions of cycles per second). |
| Processing Style | Uses massive teamwork—millions of neurons working in parallel and deeply connected. | Uses parallel processing on GPUs and TPUs but struggles with long or complex inputs that need lots of hardware power and memory. |
| Latency (Delay) | It’s designed for low delay (senses and actions connect almost instantly). | Can process fast, but can hinder due to slow network. |
| Real-Time Use | Connects the act of thinking and doing very easily. | Requires a strong link between computing and sensors (e.g., robots, self-driving cars). |
Decision-Making: Logic vs Ethics
Human Decision-Making
Follow your heart, but take your brain with you.
Does this ring a bell? We usually say this because as humans our hearts and brains equally contribute to the decisions we make, as we tend to think with both heart and mind, balancing emotion, fairness, and reason before acting.
After making a mistake, we tend to reflect upon it and learn from it in order to grow and understand what's right and wrong.
When reaching a conclusion, we keep in mind all the values and morals that we have been nurtured with.
Machine Decision-Making
Unlike our brain, machines take their next step based on the goals and data they’ve been fed.
Without a moral compass, they might choose what looks efficient but ends up hurting people or systems.
Fun fact: As per some research, it has been documented that training large language models (for example, earlier large models) uses hundreds to thousands of megawatt-hours!
The Brain Gives Us Inspiration for AGI Research
It might strike you as astonishing but, neuroscience has actually inspired many ideas in AI (e.g., hierarchical representations, reinforcement learning, and attention mechanisms).The brain inspires ideas such as step-by-step learning, positive reinforcement, and focusing attention on the real purpose. Scientists, in return, make use of AI tools to understand the mysteries of the mind.
Don't you ever wonder? How does a robot learn by doing, just as a child learns to walk by falling a few times?
- Learning and adaptation: As we learn something new, our brain changes its connections. Similarly, AI also amends its systems after making a mistake.
- Attention systems: Just as our mind tunes out the noise to focus on one voice in a crowd, AI models use “attention” to find meaning in massive data.
- Learning by doing: Robots that move, explore, and react try to mirror the way humans learn through experience.
At the end of this journey, it’s crystal clear that the human brain and AGI walk on two completely different paths. While our brain remains the origin of intelligence, AGI is more of a mirror trying to step into our shoes. So, as we continue to make smarter machinery, don’t let the fact that AGI isn’t here to replace us slide away, for it is merely here to assist us and make life easy.
Want to learn more? Contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is general intelligence?
General intelligence is the power to learn, understand, and use knowledge in many areas—not just one. It’s what helps humans think clearly, solve problems, and bend with change instead of breaking under it.
What is the future of AGI?
The future of AGI is quite auspicious; however not so certain because many people believe that it could reshape our industries, science, and everyday life. Nonetheless, like a double-edged sword, it also brings worries about control, fairness, and the fate of human jobs.
Can AGI emulate the human mind?
AGI basically seeks to mirror our brain when it comes to reasoning, learning, and creating. Yet, today’s AI remains a shadow of that dream, missing the warmth of emotion, the compass of morality, and the spark of true awareness.
Can AGI think on its own?
Not yet. Today’s AI walks the path we draw for it, following coded rules and learned patterns. The gift of true independent thought—to dream, decide, and value on its own—is still a mountain scientists are climbing.
What type of AI is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is actually a narrow AI. It is built to do only certain tasks like writing or answering questions. It speaks without any problem, yet it doesn’t think or feel as humans do—the light of self-awareness still lies beyond its reach.
Will AGI replace humans?
AGI might take over some jobs, but its true promise lies in working beside us. The aim is teamwork—machines taking care of the routine, while humans lead with creativity, heart, and thoughtful choice.
What do you mean by artificial general intelligence?
By Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) we refer to machines that are able to think, learn, and do tasks on their own with understanding, logic, and the ability to adapt. It stands as the next great leap beyond today’s narrow, single-purpose AI.



