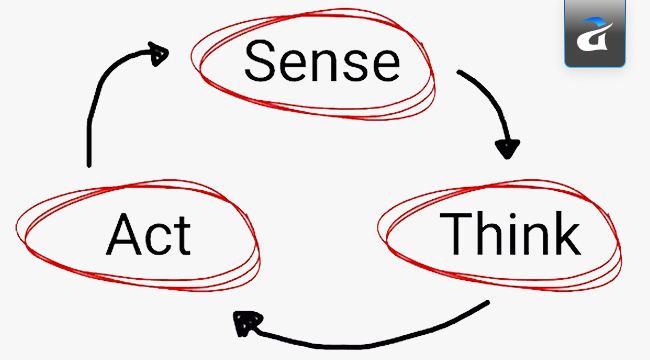
But what exactly lies in the creation of these wondrous agents? It’s called the Sense–Think–Act cycle, which powers today’s robotics and autonomous systems.
As the title speaks for itself, we can tell that it’s actually the way intelligent AI agents watch the world, make sense of it, and then move into action.

In this blog, we’ll wander through what this cycle really means, why it matters in shaping intelligent systems, and how it finds its place across industries. And so, by the end, you’ll see how this quiet cycle is the backbone and pulse of modern AI agents.
What Is the Sense-Think-Act Cycle?
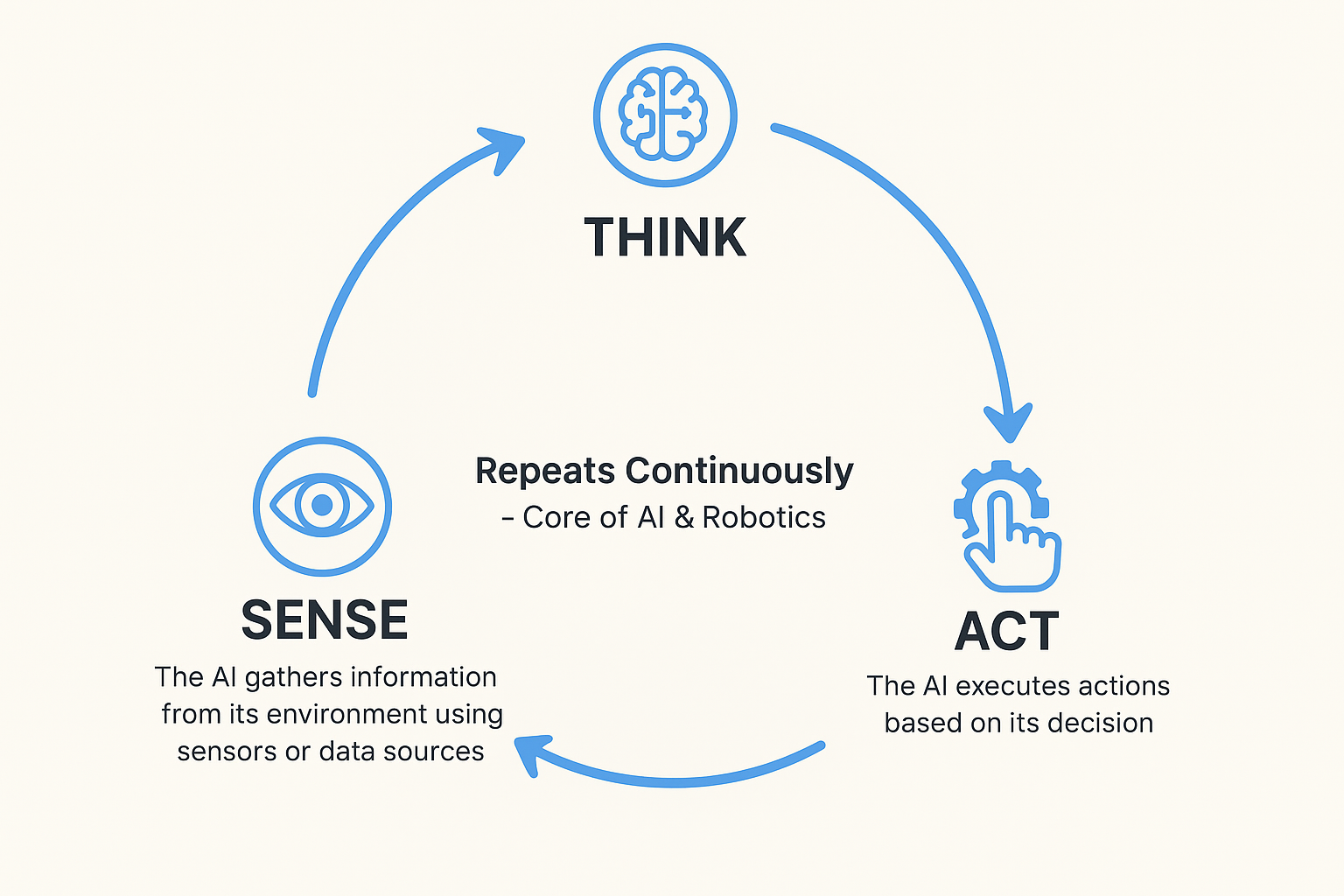
Now you may ask, what exactly is the sense-think-act-cycle?
Basically, this cycle demonstrates to us how an AI agent lives within its environment. It moves through three simple steps:
- Sense: The agent gathers information through sensor fusion or inputs.
- Think: It processes what it has received, weighs the meaning, and chooses a response.
- Act: It carries out an action that shapes the environment around it.
In plain terms, I would say that it mirrors how we, humans, see, reflect and respond.
Breaking Down the Sense-Think-Act Model
1. Sense: Gathering Information
As you might have guessed, the first step of this cycle is called “sense”Now, what exactly is it? Let’s find out.
So, an AI system starts off by collecting information from around it. For this, it uses:
- Cameras: to capture an image
- Microphones: to hear
- Sensors: to sense its surroundings
Example:
Have you ever seen a drone? It has some cameras and GPS in it, which help it sense terrain, altitude and obstacles around it.
2. Think: Processing and Decision Making
Once all the information is gathered, the agent moves onto the second process of our cycle, “think”, to process it.This stage is actually more complex than you think because the AI uses algorithms, logic, or machine learning models in order to interpret the data and choose a response.
Key tasks in the thinking phase include:
- Recognizing patterns
- Comparing current data with past data
- Predicting outcomes
- Selecting the best possible action
Example:
Let’s resume our first example: Now, the drone will start the speed and choose the best and safest route to continue.
3. Act: Executing Decisions
Last but not least, we have the “acting” step.Once the agent has made its decision, it starts to act upon it.
Here are some actions it includes:
- Moving a robot arm
- Sending a message
- Playing a sound or speaking
- Updating a database
Example:
Now that we know that the drone is wary of its surroundings and has decided to take a certain route, it will finally start to move.
Why the Sense-Think-Act Cycle Is Important for AI Agents
We can already presume that the Sense-Think-Act cycle lies at the heart of intelligent agents, seeing the roles each step has to play. It reflects the rhythm of intelligent behavior—perception, reasoning, and response.Without it, the working and interactive AI we see right now wouldn’t simply exist, or perhaps there wouldn’t be any room for it to give us more than static answers.
This cycle matters because it gives agents:
- Adaptability: to adjust when there’s a change in surroundings.
- Autonomy: act without needing support or guidance.
- Learning: the chance to refine choices with each turn of the loop.
- Reach: practical use across many fields.
Applications of the Sense-Think-Act Cycle in AI Agents
The glory of this cycle isn't merely confined to paper; instead, we witness it today with our own eyes.Here are some of its industry applications that I have compiled for you:
| Applications | Sense | Think | Act |
| Self-Driving Cars | Cameras, radar, and sensors help understand the road. | Algorithms weigh routes and risks. | The car steers, brakes, or speeds ahead. |
| Healthcare Systems | Devices gather patient data. | Software studies symptoms and compares conditions. | It suggests treatments or alerts a doctor. |
| Virtual Assistants | They listen for commands | Language models interpret meaning | They answer, set reminders, or manage smart devices. |
| Industrial Robots | Sensors track items on a belt. | Programs decide how to pick and place. | Arms move to assemble or pack. |
| Finance and Trading Bots | They scan market shifts. | Predictive models weigh patterns. | Trades are made, or signals sent. |
Here, we can clearly see every example showing us the same rhythm—sense, think, act. A loop that never stops, giving AI the pulse of interaction.
In scenorios, where many agents are working together, multi-agent coordination makes sure that all of these can work together without any issues.
The effect of Feedback on Action Agents
Have you noticed how a mere pat on our shoulder, a thumb up or simply the words, "you did great," motivates us to go further?Similarly, feedback is what keeps this cycle moving forward.
After every action, there's a subtle change, or sometimes a dramatic one, in the environment. So, when the agent senses these new conditions, it starts to think again and then acts in response. Thereby, we can see that this constant loop allows the system not only to repeat tasks but also to refine them.
For instance:
- When a self-driving car goes into “brake mode” at a red light, its sensors now register a stationary state. As the light turns green and surrounding cars move, the agent updates its understanding and adjusts speed or direction.
- A recommendation system suggests a film. If the user watches it, the system interprets this as positive reinforcement. If ignored, it learns to adjust future suggestions
So, it’s clear to us that feedback prevents the cycle from being static.
It transforms the process into a rhythm of action and response, where each turn of the loop builds knowledge, sharpens accuracy, and moves the agent closer to intelligent behavior.
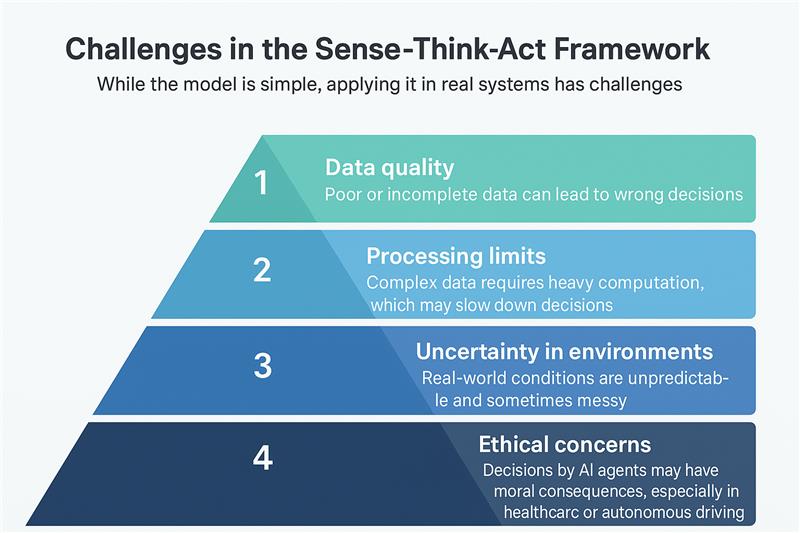
- Data quality: If you input wrong or incomplete data, then the agent’s decision can't be relied upon.
- Processing limits: If you use massive and difficult datasets, then the agent is liable to slow down.
- Uncertain environments: You might come face-to-face with some unexpected changes in difficult environments.
- Ethical concerns: AI decisions are not always correct; thus, they should be cross-checked, especially in healthcare and autonomous driving.
AI Agents Learn Through the Sense-Think-Act Cycle
You know the greatest strength of this model? It is its ability to support learning. When repeated many times, the cycle allows agents to:- Improve the accuracy of sensing
- Refine decision-making strategies
- Adapt to new environments
Similarly, many robots in factories only get better at assembling products after repeating it many times.
Thus, you see that Machine learning techniques like reinforcement learning do use this cycle
The agents sense, think then act. If they do it right, they get rewarded; or if they do it wrong, they get a penalty.
Comparing the Sense-Think-Act Model with Human Behavior
The cycle is often compared to how people function:- Sense: Eyes, ears, and other senses accumulate information.
- Think: The brain processes it and decides.
- Act: We move, speak, or respond in line with that decision.
Future of the Sense-Think-Act Cycle in AI Agents
As AI advances, the Sense-Think-Act cycle will remain its backbone, growing in depth and reach:- Better sensors will sharpen the accuracy of perception.
- Stronger algorithms will bring greater precision to decisions.
- Robotics integration will give rise to machines that act with greater independence.
- Ethical frameworks will guide these systems toward responsible use.
Conclusion
Now we know, the Sense-Think-Act cycle might sound simple on paper, but it is actually very powerful and important for AI agents and agent solution to work. How? Because it helps them to sense, process, and then act. Cherry on top, we can see AI agents progressing at adapting to their surroundings as well as learn from experience, with time, alongside taking on bigger tasks.
Want to learn more? Stay tuned with the upcoming World Summit AI (being held in Amsterdam), and contact us to get started with AI development solutions now!Frequently Asked Questions
What does ROS stand for?
ROS means Robot Operating System. It is an open-source framework that offers developers the tools and libraries to build and guide machines that move, sense, and act—like giving a robot both its language and its map.
What is an autonomous system?
A machine that can perform tasks on its own without our need is called an autonomous system. It does it by keenly observing its surroundings, carefully making a choice and acting upon it.
How to build autonomous AI agents?
If order to build an autonomous agent, three threads must be woven together: sensing, thinking, and acting. Its sensors gather the raw whispers of the world. Algorithms shape those whispers into meaning. Then, with a decision formed, the agent steps forward and acts.
What is an example of autonomous AI?
An example of autonomous AI is a customer service chatbot. These chatbots answer customer queries, guide them regarding products and solve customer issues. The best part? They are there all around the clock, without your assistance.
Are AI agents, agentic AI, and autonomous AI the same?
They walk on the same ground, yet each carries a different name. An AI agent is a system that senses and responds to its world. Agentic AI is a design where such agents are shaped to work in structured ways, often side by side. Autonomous AI is responsible for doing tasks completely on its own.