If you look at AI agents, what you see is merely the tip of the iceberg. What lies beneath the surface is much vaster than you might think, powered by advanced and specialized agents.
In our previous blog: Foundation AI agents in agentic architecture, we understood the role which these agents play in agentic architecture—read it out first if you haven’t. So, in this blog we will walk through the advanced and specialized AI agents in Agentic AI architecture.
These agents are completely capable of learning, growing, and even working together across many domains. The best part? They are not bound by fixed rules, but they live in a space of change, curiosity, and constant interaction.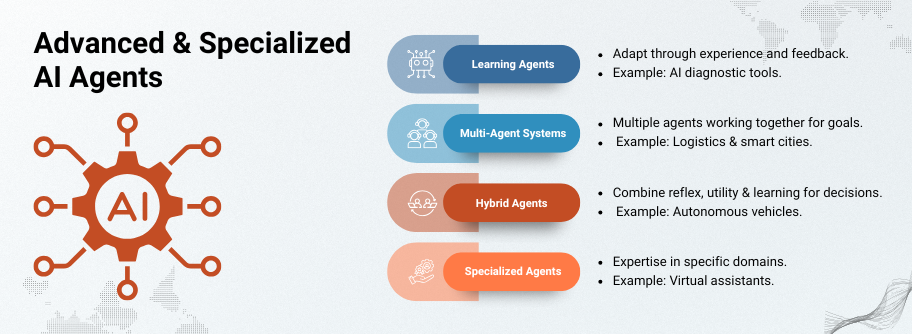
Understanding the Leap from AI Foundation to Advanced Agents
Have you ever seen how an apprentice works?
Foundational agents are just like them.
They are capable of following rules, achieving goals, and managing simple trade-offs. However, if you look at advanced agents, they’re slightly distinguished by being more like seasoned professionals or autonomous agents who learn from experience, adjust to uncertainty, and navigate interconnected systems with ease.
The shift comes in three keyways:
1. From reactivity to adaptivity: Agents improve by learning from past actions.
2. From Individual to Collective: Agents operate within coordinated networks, not alone.
3. From Fixed Roles to Hybrid Intelligence: Agents combine strengths from different types, solving problems with flexibility.
The Advanced and Specialized AI Agents
1. Learning Agents
- Learning agents Move beyond fixed instructions.
- They change strategies and improve by gathering knowledge from their surroundings. A learning element refines actions from feedback, while a performance element carries out decisions.
- Picture an AI medical diagnostic tool: with each patient, it spots patterns, corrects mistakes, and hones its precision. This makes it a powerful AI agent tool here.
2. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
How They Work
- Multi-agent systems tend to bring together myriad of AI agents that cooperate or compete in the same environment.
- Each of these agents has its own goal to accomplish, yet together they can produce intelligence beyond any single agent.
- Imagine a logistics network: one agent manages stock, another plans how goods move, and other tracks orders. Together, these smart agents keep operations smooth and efficient.
3. Hybrid Agents
How They Work
- Well, if you pour all the strength of reflex, utility-based and learning agents in a blender, the outcome would be hybrid agents.
- These agents have layers, a reactive layer for quick responses and a deliberative layer for planning and making thoughtful decisions.
- Imagine an autonomous car which is powered by a robotic control system: it brakes instantly for sudden events (reflex), chooses routes (planning), uses fuel efficiently (utility-based), and improves from experience (learning).
4. Specialized Agents
Specialized agents are designed for tasks that need deep, specific knowledge. Unlike general-purpose agents, they perform best in focused, narrow areas.Types of Specialized Agents
1. Interface Agents: Connect humans with systems, making interactions easier.
Example: Virtual assistants and personal assistants guiding users through complex software.
2. Information Agents: Gather, filter, and manage data.
Example: Search engines and recommendation engines.
3. Collaborative Agents: Work alongside human teams, coordinating tasks.
Example: AI project management tools offer you a scalable AI agent solution.
4. Mobile Agents: Move across networks or systems to complete tasks.
Example: Security monitoring agents in distributed systems.
5. Social Agents: Interact with humans in natural, socially aware ways.
Example: Chatbots with advanced conversational skills.
An overview of AI agents:
| AI agents | Strengths | Limitations | Use cases |
| Learning Agents | Evolve over time, relying less on pre-coded rules. Function well in changing or unpredictable settings. Improve continuously without needing external updates | Need large amounts of data to be accurate. Can overfit, learning too narrowly from limited examples. Pose ethical concerns if trained on biased data. | Healthcare: Diagnosis tools that refine predictions with experience. Finance: Fraud detection systems learning from shifting threats. Education: Tutoring systems adjusting to each student’s pace. |
| Multi-Agent-Systems (MAS) | Can handle large systems with many moving parts. Solve problems through shared effort. Build reliability by avoiding dependence on a single agent. | Build reliability by avoiding dependence on a single agent. Coordination can be tricky if agents’ goals conflict. It’s liable of giving potentially slow performance due to the demands of communication. | Smart Cities: Traffic agents controlling lights, vehicles, and pedestrians. E-commerce stores: Used for recommendation of products. Robotics: A lot of robots complete coordinated tasks. |
| Hybrid agents | Can respond quickly while thinking ahead. | The structure is detailed and uses many resources. | Autonomous vehicles that combine reflexive braking with smart route choices. |
| Specialized agents | Highly effective in their specific domain. | Do not adapt well outside their specialty. | Healthcare Agent: A smart guide that reads patient data to suggest care designed for each individual. Financial Trading Agent: A fast thinker that rides shifting markets to make timely and strategic trades. |
Advanced Agents Powering Agentic Systems and framework
Are you also wondering how advanced agents power agentic systems? These advanced agents are not standalone innovations—they represent the next layer in agentic framework. When embedded into systems, they:
- Enable self-learning ecosystems ensuring growth and adaptability.
- Unlock collective intelligence through multi-agent collaboration.
- Deliver end-to-end autonomy with hybrid and specialized integration.
Applications across Industries
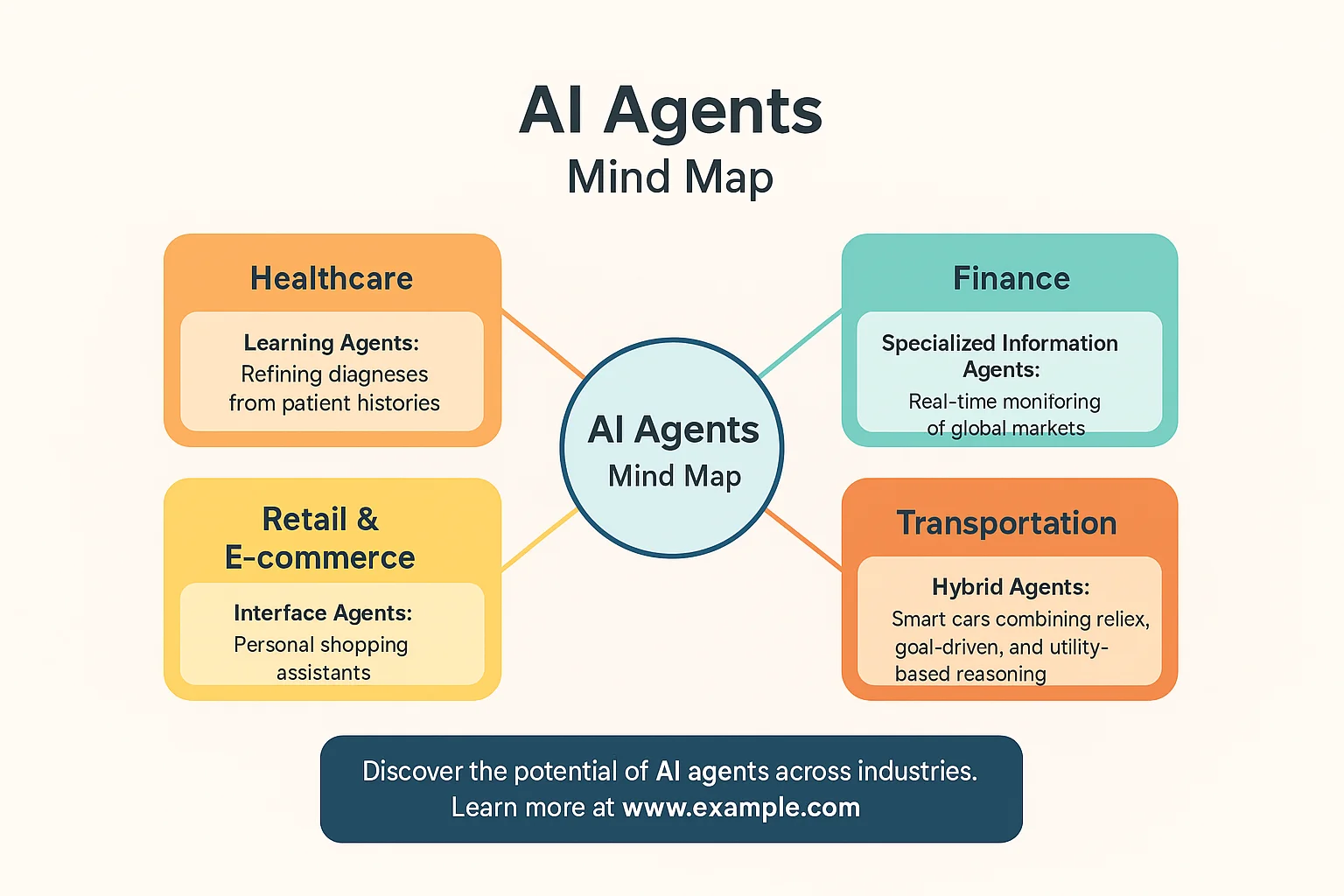
Healthcare
- Learning Agents: Refining diagnoses from patient histories.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Coordinating hospital workflows (doctor scheduling, patient monitoring, drug supply).
- Hybrid Agents: Powering robotic surgeons with reflexes and strategic planning.
Finance
- Specialized Information Agents: Real-time monitoring of global markets.
- Learning Agents: Fraud detection learning from new fraud patterns.
- Hybrid agents balance portfolios like seasoned jugglers, weighing risks, goals, and shifting data all at once.
Retail & E-commerce
- Multi-agent systems : orchestrate supply chains and delivery routes like conductors guiding a grand symphony.
- Interface Agents: Personal shopping assistants.
- Learning Agents: Adapting product recommendations to shifting customer trends.
Transportation
- Hybrid Agents: Smart cars combining reflex, goal-driven, and utility-based reasoning are an example of agentic automation.
- Multi-Agent Systems coordinate fleet management across cities.
- Mobile Agents: Ticketing systems moving across platforms.
Enterprise & Technology
- Collaborative agents stand beside teams like quiet partners, helping manage projects and guide decisions.
- Social agents greet customers with warmth, weaving empathy into digital conversations.
- ?Hybrid Agents powering enterprise-level resource outsourcing platforms.
The Challenges Ahead
As with all progress, advanced agents bring hurdles:- Ethical Concerns: Biased data in learning agents can reinforce inequalities.
- Complexity Costs: Multi-agent and hybrid systems demand immense computational power.
- Security Risks: Mobile and social agents open doors to exploitation.
- Human Trust: Ensuring explainability of AI decisions is critical for adoption, especially when comparing agentic and non-agentic systems.
The Future of Advanced Agents in Agentic Systems
Looking ahead, advanced agents point toward:- Hyper-personalized systems that learn with each user.
- Global-scale coordination, such as climate modeling with multi-agent networks.
- A workspace where humans and AI stand side by side—specialized minds and social voices acting not as tools, but as true co-workers.
Conclusion
In this blog, we stepped onto a richer stage—where learning agents grow wiser, multi-agents work in harmony, hybrids blend strengths, and domain experts shine with mastery. They are the quiet builders of adaptability, teamwork, and deep understanding. Want access to the best AI solutions? Contact us now.
Want to learn more about AI? Stay connected with the upcoming event, world summit AI held in Amsterdam.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are agentic AI and AI agents?
Agentic AI is artificial intelligence designed to act with purpose. It doesn’t just respond; it decides, plans, and carries tasks through. An AI agent is the working part of this idea—like a digital envoy that observes the world, reasons with what it knows, and acts on its own.
What is an example of an agentic AI system?
You already know it; The most common example is a self-driving car. It can easily read the road, weigh its choices, and turn the wheel without being given constant instructions. It shows how machines can move beyond following commands into making decisions.
Is ChatGPT an AI Agent?
ChatGPT is not a full agent. It is a language model, it helps people from all around the world by answering their queries, performing tasks and even doing coding. However, on its own, it does not sense, decide, and act in the world the way an agent would.
What is the best agentic AI?
There isn’t a single “best.” Different agentic AIs excel in different spaces—some manage factories, others guide financial markets, and some help scientists uncover new cures. The best depends on the work at hand.
Which is the most powerful AI agent?
Have you heard of complex systems? Agents which are built on complex systems are considered the most powerful AI agents today, like autonomous robots, advanced trading bots, or multi-agent research platforms. Power here means reach: their ability to act across many tasks, adapt, and keep learning.



